A rare case of caries sicca right shoulder
Ankur Salwan, Amit Saoji
Corresponding author: Ankur Salwan, Department of Orthopedics, Datta Meghe Institute of Medical Sciences, Wardha, Maharashtra, India 
Received: 09 Jul 2022 - Accepted: 02 Sep 2022 - Published: 05 Sep 2022
Domain: Orthopedic surgery
Keywords: Caries sicca, tuberculosis, humeral head, extrapulmonary, abduction
©Ankur Salwan et al. PAMJ Clinical Medicine (ISSN: 2707-2797). This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution International 4.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Cite this article: Ankur Salwan et al. A rare case of caries sicca right shoulder. PAMJ Clinical Medicine. 2022;10:3. [doi: 10.11604/pamj-cm.2022.10.3.36266]
Available online at: https://www.clinical-medicine.panafrican-med-journal.com//content/article/10/3/full
A rare case of caries sicca right shoulder
&Corresponding author
Caries sicca is the classic dry form of tuberculosis of proximal humerus. Caries sicca is a fairly rare extrapulmonary presentation of bone tuberculosis. It accounts for 0.9 to 1.7 percent of all extrapulmonary tuberculosis cases. A 23-year-old female presented to the orthopaedics outpatient department with complaint of pain and restriction of shoulder movements for 6 months. The patient has no history of tuberculosis previously, but has a history of a family member suffering from pulmonary Koch. On clinical examination there was tenderness over the Greater tuberosity with restricted external rotation, abduction up to 30 degrees with further passive abduction being painful. There was marked wasting of deltoid and other muscles. Patient´s biopsy was taken for histopathology which showed normal morphology of bony trabeculae, fibromuscular and fatty tissue infiltration of chronic inflammatory cells and at places epithelioid granuloma with Langhans giant cells and caseous necrosis which favor the diagnosis of tuberculosis. The patient was started on chemotherapy antitubercular drugs with intensive phase of 2 months and continuation phase of 7 months. During the treatment period the patient was followed up and the satisfactory shoulder movements abduction up to 90 degrees was achieved after 9 months and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) was considered as a prognostic factor for treatment.
Figure 1: a rare case of caries sicca and its prognosis with chemotherapy; (A) Gross deformity of the humeral head showing periarticular osteopenia, peripheral osseous erosions, gradual narrowing of interosseous space (Phemister's triad); (B) X-ray after 4 months of treatment shows improved humeral head and articulating surface; (C) post-treatment X-ray after nine months of treatment shows improved osteopenia and restoration of the humeral head; (D) post-treatment clinical photo showing normal shoulder contour; (E,F) histopathological picture showing granulomas with caseous necrosis suggestive of tuberculosis
Search
This article authors
On Pubmed
On Google Scholar
Citation [Download]
Navigate this article
Similar articles in
Key words
Tables and figures
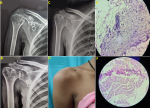 Figure 1: a rare case of caries sicca and its prognosis with chemotherapy; (A) Gross deformity of the humeral head showing periarticular osteopenia, peripheral osseous erosions, gradual narrowing of interosseous space (Phemister's triad); (B) X-ray after 4 months of treatment shows improved humeral head and articulating surface; (C) post-treatment X-ray after nine months of treatment shows improved osteopenia and restoration of the humeral head; (D) post-treatment clinical photo showing normal shoulder contour; (E,F) histopathological picture showing granulomas with caseous necrosis suggestive of tuberculosis
Figure 1: a rare case of caries sicca and its prognosis with chemotherapy; (A) Gross deformity of the humeral head showing periarticular osteopenia, peripheral osseous erosions, gradual narrowing of interosseous space (Phemister's triad); (B) X-ray after 4 months of treatment shows improved humeral head and articulating surface; (C) post-treatment X-ray after nine months of treatment shows improved osteopenia and restoration of the humeral head; (D) post-treatment clinical photo showing normal shoulder contour; (E,F) histopathological picture showing granulomas with caseous necrosis suggestive of tuberculosis




