A rare case of congenital upper limb deformity in a neonate
Shrut Vasavada, Parth Shah
Corresponding author: Shrut Vasavada, Department of Orthopedics, Datta Meghe Institute of Medical Sciences, Wardha, Maharashtra, India 
Received: 05 Jan 2023 - Accepted: 01 Feb 2023 - Published: 17 Feb 2023
Domain: Neonatology,Pediatric surgery
Keywords: Radial club hand, radial dysplasia, thumb hypoplasia
©Shrut Vasavada et al. PAMJ Clinical Medicine (ISSN: 2707-2797). This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution International 4.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Cite this article: Shrut Vasavada et al. A rare case of congenital upper limb deformity in a neonate. PAMJ Clinical Medicine. 2023;11:41. [doi: 10.11604/pamj-cm.2023.11.41.38761]
Available online at: https://www.clinical-medicine.panafrican-med-journal.com//content/article/11/41/full
A rare case of congenital upper limb deformity in a neonate
&Corresponding author
Radial club hand or radial dysplasia is an uncommon congenital anomaly. It is a longitudinal deficiency along the preaxial or the radial aspect of the upper extremity. It includes a wide spectrum of disorders that encompass an absent thumb, thumb hypoplasia, a thin first metacarpal and an absent radius. A 20-day-old male child, a baby of Vishakha Pravin Dongare was brought to the out-patient department at Acharya Vinoba have rural hospital, Wardha, Maharashtra with complaints of fever for 2 days. There was a history of a deformed left upper limb in the form of a short, curved, left forearm and an absent thumb since birth. The movements of the left elbow were limited. All the distal movements including the rotatory movements of the forearm and the wrist and the fine finger movements were not elicited. Only flickering movements of the fingers were elicited. The thumb had not developed at all. On clinico-radiological examination it was found that there was a complete deficiency of radius and the thumb with hyperflexion and radial side deviation at the wrist joint. Currently, the patient is under observation and will be followed up at monthly intervals for further evaluation and management.
Figure 1: neonate with left sided radial dysplasia and thumb hypoplasia and comparing it with the normal contralateral side; A) deformity of left upper limb with radial deviation and hyperflexion at wrist and absent thumb; B) deformity of left upper limb normal ulna; C) deformity of left upper limb with hyper-palmar flexion with crowding of fingers; D) comparison of the normal limb with the abnormal limb; E) X-ray showing deficiency of radius and thumb
Search
This article authors
On Pubmed
On Google Scholar
Citation [Download]
Navigate this article
Similar articles in
Key words
Tables and figures
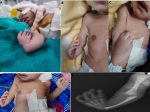 Figure 1: neonate with left sided radial dysplasia and thumb hypoplasia and comparing it with the normal contralateral side; A) deformity of left upper limb with radial deviation and hyperflexion at wrist and absent thumb; B) deformity of left upper limb normal ulna; C) deformity of left upper limb with hyper-palmar flexion with crowding of fingers; D) comparison of the normal limb with the abnormal limb; E) X-ray showing deficiency of radius and thumb
Figure 1: neonate with left sided radial dysplasia and thumb hypoplasia and comparing it with the normal contralateral side; A) deformity of left upper limb with radial deviation and hyperflexion at wrist and absent thumb; B) deformity of left upper limb normal ulna; C) deformity of left upper limb with hyper-palmar flexion with crowding of fingers; D) comparison of the normal limb with the abnormal limb; E) X-ray showing deficiency of radius and thumb




