Anomalie du disque de gloire du matin
Rim El Hachimi, Rida El Hadiri
Corresponding author: Rim El Hachimi, Mohamed V University of Rabat, Department of Ophthalmology A, Speciality Hospital of Rabat, Morocco 
Received: 18 Dec 2021 - Accepted: 06 Jan 2022 - Published: 13 Jan 2022
Domain: Ophthalmology
Keywords: Gloire du matin, anomalie congénitale, papille optique
©Rim El Hachimi et al. PAMJ Clinical Medicine (ISSN: 2707-2797). This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution International 4.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Cite this article: Rim El Hachimi et al. Anomalie du disque de gloire du matin. PAMJ Clinical Medicine. 2022;8:8. [doi: 10.11604/pamj-cm.2022.8.8.32880]
Available online at: https://www.clinical-medicine.panafrican-med-journal.com//content/article/8/8/full
Anomalie du disque de gloire du matin
Morning glory disc anomaly
&Auteur correspondant
We here report the case of a male child aged 8 years with no specific history, presenting with nystagmus and strabismus. Fundus examination showed enlarged, retracted orange-colored optic disc with white fibroglial tissue at its center. Major retinal vessels originated from the peripheral edge of the optical disc, extended radially to the peripapillary retina along an abnormally straight path and were hidden centrally by the tuft of white tissues. The diagnosis of congenital papillary anomaly, known as morning glory, was made. This anomaly is a congenital, funnel-shaped staphylomatous excavation of the peripapillary retina and optic nerve involving the optic disc which may be associated with eye and brain anomalies and may be characterized by a syndromic presentation.
Key words: Morning glory, congenital anomaly, optic disc
Il s´agit d´un enfant de sexe masculin âgé de 8 ans, sans antécédents particuliers qui consulte pour un nystagmus et un strabisme. L´examen retrouve un nystagmus bilatéral avec une myopie extrême. L´acuité visuelle est réduite à compte les doigts en OS. L´examen du fond œil une papille optique agrandie de couleur orange en retrait avec du tissu fibroglial blanc en son centre. Un anneau péripapillaire sous-rétinien de la zone choriorétinienne entoure le disque. Les principaux vaisseaux rétiniens naissent du bord périphérique du disque optique et s'étendent radialement selon un trajet anormalement droit sur la rétine péripapillaire et sont cachés au centre par la touffe de tissus blancs. La rétinophotographie est légèrement brouillée à cause du nystagmus et de la myopie extrême. L´anomalie papillaire morning glory est une excavation congénitale staphylomateuse en forme d'entonnoir de la rétine péripapillaire et du nerf optique impliquant le disque optique. L´atteinte est le plus souvent unilatérale et rare chez les Afro-Américains. L'acuité visuelle est souvent inférieure à 20/200 avec un déficit pupillaire afférent et un défaut du champ visuel. Peut être associée à des atteintes du SNC (Encéphalocèle basale transsphénoïdale) et à d´autres syndromes (CHARGE). Sur le plan oculaire, la principale complication associée est le décollement de rétine exsudatif. Le traitement de l'amblyopie associée peut entraîner une certaine récupération de la vision.
Figure 1: l´examen retrouve une papille optique agrandie de couleur orange en retrait avec du tissu fibroglial blanc en son centre. Un anneau péripapillaire sous-rétinien de la zone choriorétinienne entoure le disque. Les principaux vaisseaux rétiniens naissent du bord périphérique du disque optique et s'étendent radialement selon un trajet anormalement droit sur la rétine péripapillaire et sont cachés au centre par la touffe de tissus blancs. La rétinophotographie est légèrement brouillée à cause du nystagmus et de la myopie extrême
Search
This article authors
On Pubmed
On Google Scholar
Citation [Download]
Navigate this article
Similar articles in
Key words
Tables and figures
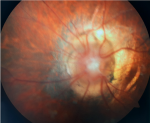 Figure 1: l´examen retrouve une papille optique agrandie de couleur orange en retrait avec du tissu fibroglial blanc en son centre. Un anneau péripapillaire sous-rétinien de la zone choriorétinienne entoure le disque. Les principaux vaisseaux rétiniens naissent du bord périphérique du disque optique et s'étendent radialement selon un trajet anormalement droit sur la rétine péripapillaire et sont cachés au centre par la touffe de tissus blancs. La rétinophotographie est légèrement brouillée à cause du nystagmus et de la myopie extrême
Figure 1: l´examen retrouve une papille optique agrandie de couleur orange en retrait avec du tissu fibroglial blanc en son centre. Un anneau péripapillaire sous-rétinien de la zone choriorétinienne entoure le disque. Les principaux vaisseaux rétiniens naissent du bord périphérique du disque optique et s'étendent radialement selon un trajet anormalement droit sur la rétine péripapillaire et sont cachés au centre par la touffe de tissus blancs. La rétinophotographie est légèrement brouillée à cause du nystagmus et de la myopie extrême




